Human survival has been changed from the old practice of variolation to the modern wonders of mRNA to include the viral vaccines. Nowadays, when science moves at the quick pace in the laboratories and plants all over the world, these вакцина continue to be an integral part of the public health. But what is put into it in order to make them? Why are they so crucial? And how does tdap vaccine и столбняк shot fit in the big viral immunity puzzle?
Let’s travel, thorough, revealing, and let’s face it, exciting, in the very complex world of these vaccines.
What Is a Viral Vaccine?
А viral vaccine can be classified as a biological form of preparation that is meant to offer immunity against a virus. It activates the body to immune to viral pathogens causing the disease without.
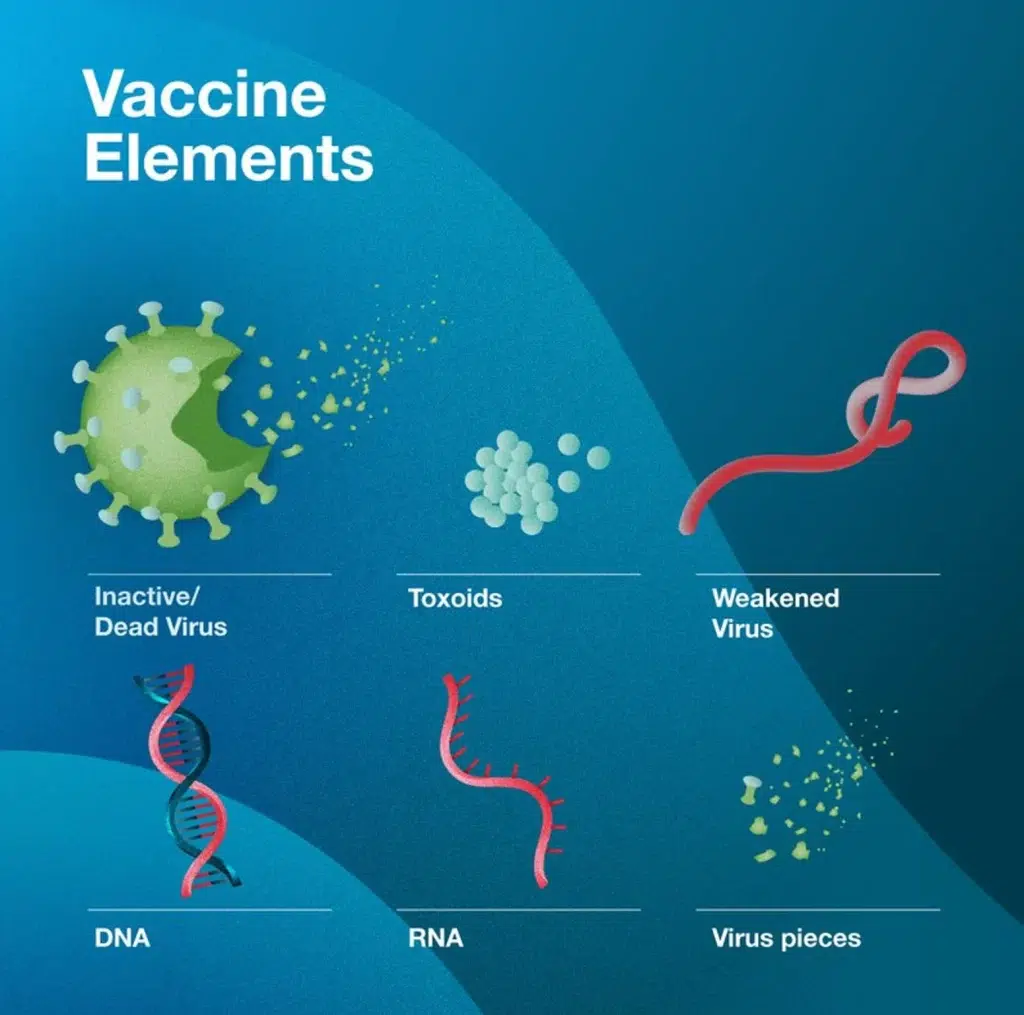
Types of Viral Vaccines:
- Live-attenuated vaccines: Contain less powerful form of the viruses (for example, measles, mumps).
- Inactivated vaccines: Use heat- or chemicals-sensitive viruses (e.g., polio).
- Subunit vaccines: Such parts of the virus as hepatitis B protein spikes (e.g., hepatitis B).
- mRNA vaccines: Train cells on how to produce viral proteins (example; COVID-19 vaccines).
- Viral vector vaccines: Take advantage of harmless viruses as tools to deliver genetic material (equivalent of a Johnson & Johnson COVID vaccine).
These vaccines aid the immune system in practicing, by putting in practice viral infections but without the negative consequences.
A Short Account of the Viral Immunization
Let’s rewind a few centuries:
- 1796: Edward Jenner used cow-pox for prevention of small-pox. This was the first viral vaccine which was successful.
- 1955: Jonas Salk announced the inactivated polio vaccine, a game-changer of world health.
- 1980: WHO announced the smallpox’s eradication, but only with the help of vaccines.
- 2020: mRNA vaccines made the news at the time of COVID-19 pandemic as they revolutionized speed and scalability.
Every step that we made helped us approach controlling some of the most murderous diseases in the history of mankind.
How the viral vaccines work in the body?
Step-by-step immune activation:
- Introduction of Antigen: The vaccine is made up viral particles or genetic code.
- Immune System Response: The White blood cells recognize the intruder and secret antibodies.
- Memory Cell Creation: The body keeps the knowledge in stock to behave more promptly than on the previous occasion.
- Immunity: When the real virus penetrates later, the same is neutralized before disease sets in by the immune system.
This so-called “immune training” may require years, or even for the whole life.

Наука, лежащая в основе разработки вакцин
Coming up with a viral vaccine is a long journey of more than a few years:
- Exploratory Stage: Laboratory studies to look for targets of the viruses.
- Pre-clinical Testing: Safety and immune response are tested by animal models.
- Clinical Trials (Phases I-III):
- Phase I: Safety on a small group.
- Phase II: Dosage and immune response testing.
- Phase III: Large-scale testing for effectiveness.
- Regulatory Review: The data is reviewed by national bodies (FDA, EMA) etc.
- Mass Production: Bioreactors scale up the process.
- Distribution & Monitoring: The global networks guarantee the access to provision and post-marketing surveillance.
Each of the steps is very careful, so that safety is never in question.
Contribution of Bioreactors in Viral Vaccines Manufacturing Industries
Bioreactors are the beating life of the modern vaccine production. In BaiLun Bio’s bioreactors are highly advanced and play a great role in:
- Culturing virus-infected cells
- Controlling the temperature, the oxygen level and the pH level.
- Scaling of lab batches to mass volumes.
- Making sure that consistency is consistent for thousands of liters
Their level of precision allows the pharmaceuticals companies to respond to the global demand, without compromising on quality.
Popular Viral Vaccines That You Should Know
1.COVID-19 Vaccines
The world pandemic had made everyone a mini vaccine specialist. From Pfizer’s mRNA to China’s inactivated Sinovac, these vaccines showed the force of a fast-passed science and joint efforts of the planet.
2.Influenza Vaccines
Direct action against relapses in the flu vaccines is performed annually and adjusted accordingly through the circulating strains. They save a lot of lives, particularly in the weak population.
3.Hepatitis B Vaccine
This sub unit viral vaccine is long lived against a virus, which causes chronic liver disease and cancer.
4.HPV Vaccine
Attacks the human papillomavirus, hence preventing cervical and other cancers.
5.Measles, Mumps, Rubella (MMR) Vaccine
A live-attenuated vaccine that works conjointly which has caused significant reduction of such common childhood diseases.
The Ways in Which Tdap Vaccine and Tetanus Shot Ties In
Also, not viral, the tdap vaccine, и tetanus shot are frequently talked about on the same platforms with viral vaccines in regards to the part they play in routine immunization.
Grading of the tdap vaccine protects one from tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (whooping cough). Tetanus shot provides temporary protection against a bacterial poison that is present in the soil.
These vaccines are crucial in the emergency care and prenatal healthcare. And yes, the majority of immunization companies produce them in combination with the viral vaccines in multifunctional facilities.
Global Leaders in Vaccine Manufacturing
Vaccination manufacturers cross the continents, mixing biotechnology with logistics on grand scale.
Top players include:
- Pfizer/BioNTech (USA/Germany)
- Sinovac and Sinopharm (China)
- Serum Institute of India (India)
- Moderna (USA)
- Sanofi Pasteur (France)
- Johnson & Johnson (USA)
Each provides millions of doses each year with help from bioreactors, purification systems, and high controls of quality.

Distribution Challenge and Cold Chain Management
Production of viral vaccines is only a half of the war. Distributing it around all corners in the world is another tale.
Challenges include:
- Cold chain logistics for the temperature sensitive vaccines
- Geopolitical barriers
- Vaccine hesitancy fueled by misinformation
- Limited infrastructure in remote areas
Solutions include the use of digital tracking, solar refrigeration and local manufacturing partnership.
Safety, Side Effects, and Trust of Public Through Viral Vaccines
Even though one may come up with a scientifically sound viral vaccine, its effectiveness is dependent on trust and safety monitoring from the public. Appreciation of possible side effects and transparency in communication are the cornerstones for expanding uptake of vaccination across the world.
Common Side Effects:
- Mild fever
- Soreness or redness on the site of injection
- Fatigue
- Headache or body aches
These are the indications that the immune system is reacting and they are temporary.
Rare but Serious Reactions:
- Allergic reactions (anaphylaxis)
- The Myocarditis (only in a few of the mRNA COVID vaccines virtually never).
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (associated with a couple of viral or bacterial infections after vaccination)
- Remarkable events of such kind are always under surveillance by agencies such as CDC, WHO, and local health bodies.
The Future of Viral Vaccines
What’s on the horizon?
- Individualized vaccines against such diseases like HIV and cancer.
- The vaccines that can be applied to different variants of pan-coronavirus.
- Vaccines made from plants which are grown in genetically modified crops.
- Needle-free delivery methods: nasal sprays, skin patches.
The future is bright and fast and more efficient, it is achieved through innovations and biotechnological evolution.
How BaiLun Bio helps to produce viral vaccines?
БайЛун Био does not have just equipment for sale, but also more. You will find knowledge, innovation, and commitment to saving global health.
Offerings include:
- Laboratory fermenters for R&D
- Industrial-scale bioreactors for viral production
- CIP/SIP systems
- Process control automation
- Custom configuration for viral lines of vaccine.
Their products run the world’s leading vaccination makes and immunization firms.
Final Thoughts
From these microscopic starts in a lab dish to life-saving shots to your arm, viral vaccines are one of humankind’s greatest weapons. They are much higher than medicine, they are milestones in human development protecting billions from disease, disability, and death.
There also has to be the synergy between the manufacturers of the vaccination, the immunization companies and high performance bioprocessing technology, as the biotech evolves.
If you are looking to embark on this mission, you may start with the right equipment. Find out more on vaccine manufacturing solutions on BaiLun Bio and move your process up a notch.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Q1: What amount of time is required in the creation of viral vaccine?
Typically, 8–15 years. In such emergencies as COVID-19, it can be expedited with overlapping phases of trials and regulatory engagements.
Q2: Is mRNA vaccines viral?
Yes, they doing so, as they protect against viruses by instructing the immune system, with the use of genetic instructions of the virus.
Q3: When should I get tdap vaccine or tetanus shot?
The tdap vaccine should be taken by grown-ups after a decade or after the chance of coming into contact with possible infection through injury.
Q4: Is viral vaccines’ combination possible into one shot?
Yes. The MMR vaccine comprises of measles, mumps and rubella. Some work is being done into combo COVID-flu shots.
Q5: Is live-attenuated type of vaccination safe for all?
However, they are usually safe although not recommended for the immunocompromised ones because of live nature.